

A complete AMQP has three main components a broker, a consumer, and a producer. RabbitMQ is used as a message broker to implement advanced messaging queuing protocol (AMQP). Headers - it ignores the routing key and looks at the headers that sent with the message.It is applied when sending a message to individuals-for example, sending notifications to individuals in a specific geographical location. The queue has to be the same as the routing key. Direct - delivers messages to queues based on a message routing key.RabbitMQ will use this scenario to distribute messages to the different participants of that specific group. An excellent example of Fanout Exchange is a Group chat. Fanout - routes messages to all the queues bound to it, and the routing key is ignored.

For example, distribute data specific to a geographical location depending on another factor such as point of sale.
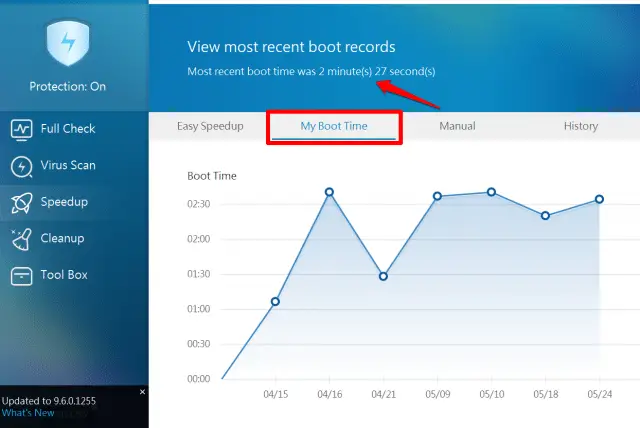
In this case, each produced message needs to have a virtual address key that the exchange will use to determine which queue the message should be routed to. Routing Key - a RabbitMQ can have many message queues.
Dcoker compose increase startup time pdf#
Here is a simple scenario of a user sending a request (message) to create a PDF web application (producer)įor the four components to effectively communicate, the following properties will be essential in determining the message destination. Consumer - application or a service that reads messages from the RabbitMQ server queue.Queue - a RabbitMQ buffer that stores published messages.When the messages arrive at the telephone exchange, the Exchange determines the target consumer for a particular message and routes accordingly. It receives messages from producers and publishes them in queues using routing rules to send them to a consumer.įor example, take the case of the typical telephone Exchange for call routing. Exchange - it acts as a message filter.A producer (publisher) - an application or a service that publishes a message to a RabbitMQ server.There are significant components that facilitate RabbitMQ message brokerage between the consumer and the producer. In this case, we will have a RabbitMQ server. So instead of the producer calling consumer service directly, we set up another server that acts as the broker between the two.

The consumer is the application or service which will be receiving the messages. As we said, the producer is the application or service which is sending messages. RabbitMQ architecture is made up of a producer and consumer. RabbitMQ architecture and essential components Many producers can submit messages to queues, and consumers can attempt to get messages from these queues. A queue is a huge message buffer built upon the first-in, first-out(FIFO) principle. These messages are maintained in a queue. It is a message broker that receives messages from senders (producer) and forwards them to receivers (consumer). RabbitMQ is an open-source distributed message queue that supports many communication protocols.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
